
前言
用过 Node.js 开发过的同学肯定都上手过 koa,因为他简单优雅的写法,再加上丰富的社区生态,而且现存的许多 Node.js 框架都是基于 koa 进行二次封装的。但是说到性能,就不得不提到一个知名框架:fastify ,听名字就知道它的特性就是快,官方给出的Benchmarks甚至比 Node.js 原生的 http.Server 还要快。
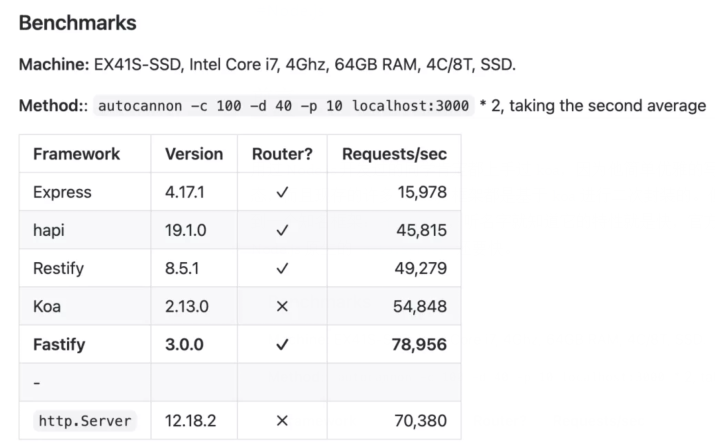
Benchmarks
性能提升的关键
我们先看看 fastify 是如何启动一个服务的。
# 安装 fastify
npm i -S fastify@3.9.1
// 创建服务实例
const fastify = require(\’fastify\’)()
app.get(\’/\’, {
schema: {
response: {
// key 为响应状态码
\’200\’: {
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
hello: { type: \’string\’ }
}
}
}
}
}, async () => {
return { hello: \’world\’ }
})
// 启动服务
;(async () => {
try {
const port = 3001 // 监听端口
await app.listen(port)
console.info(`server listening on ${port}`)
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
process.exit(1)
}
})()
从上面代码可以看出,fastify 对请求的响应体定义了一个 schema,fastify 除了可以定义响应体的 schema,还支持对如下数据定义 schema:
body:当为 POST 或 PUT 方法时,校验请求主体;
query:校验 url 的 查询参数;
params:校验 url 参数;
response:过滤并生成用于响应体的 schema。
app.post(\’/user/:id\’, {
schema: {
params: {
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
id: { type: \’number\’ }
}
},
response: {
// 2xx 表示 200~299 的状态都适用此 schema
\’2xx\’: {
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
id: { type: \’number\’ },
name: { type: \’string\’ }
}
}
}
}
}, async (req) => {
const id = req.params.id
const userInfo = await User.findById(id)
// Content-Type 默认为 application/json
return userInfo
})
让 fastify 性能提升的的秘诀在于,其返回 application/json 类型数据的时候,并没有使用原生的 JSON.stringify,而是自己内部重新实现了一套 JSON 序列化的方法,这个 schema 就是 JSON 序列化性能翻倍的关键。
如何对 JSON 序列化
在探索 fastify 如何对 JSON 数据序列化之前,我们先看看 JSON.stringify 需要经过多么繁琐的步骤,这里我们参考 Douglas Crockford (JSON 格式的创建者)开源的 JSON-js 中实现的 stringify 方法。
“JSON-js:https://github.com/douglascrockford/JSON-js/blob/master/json2.js
// 只展示 JSON.stringify 核心代码,其他代码有所省略
if (typeof JSON !== “object”) {
JSON = {};
}
JSON.stringify = function (value) {
return str(“”, {“”: value})
}
function str(key, holder) {
var value = holder[key];
switch(typeof value) {
case “string”:
return quote(value);
case “number”:
return (isFinite(value)) ? String(value) : “null”;
case “boolean”:
case “null”:
return String(value);
case “object”:
if (!value) {
return “null”;
}
partial = [];
if (Object.prototype.toString.apply(value) === “[object Array]”) {
// 处理数组
length = value.length;
for (i = 0; i < length; i = 1) {
// 每个元素都需要单独处理
partial[i] = str(i, value) || “null”;
}
// 将 partial 转成 ”[…]“
v = partial.length === 0
? “[]”
: “[” partial.join(“,”) “]”;
return v;
} else {
// 处理对象
for (k in value) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(value, k)) {
v = str(k, value);
if (v) {
partial.push(quote(k) “:” v);
}
}
}
// 将 partial 转成 “{…}”
v = partial.length === 0
? “{}”
: “{” partial.join(“,”) “}”;
return v;
}
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出,进行 JSON 对象序列化时,需要遍历所有的数组与对象,逐一进行类型的判断,并对所有的 key 加上 “”,而且这里还不包括一些特殊字符的 encode 操作。但是,如果有了 schema 之后,这些情况会变得简单很多。fastify 官方将 JSON 的序列化单独成了一个仓库:fast-json-stringify,后期还引入了 ajv 来进行校验,这里为了更容易看懂代码,选择看比较早期的版本:0.1.0,逻辑比较简单,便于理解。
“fast-json-stringify@0.1.0:https://github.com/fastify/fast-json-stringify/blob/v0.1.0/index.js
function $Null (i) {
return \’null\’
}
function $Number (i) {
var num = Number(i)
if (isNaN(num)) {
return \’null\’
} else {
return String(num)
}
}
function $String (i) {
return \'”\’ i \'”\’
}
function buildObject (schema, code, name) {
// 序列化对象 …
}
function buildArray (schema, code, name) {
// 序列化数组 …
}
function build (schema) {
var code = `
\’use strict\’
${$String.toString()}
${$Number.toString()}
${$Null.toString()}`
var main
code = buildObject(schema, code, \’$main\’)
code = `;return $main`
return (new Function(code))()
}
module.exports = build
fast-json-stringify 对外暴露一个 build 方法,该方法接受一个 schema,返回一个函数($main),用于将 schema 对应的对象进行序列化,具体使用方式如下:
const build = require(\’fast-json-stringify\’)
const stringify = build({
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
id: { type: \’number\’ },
name: { type: \’string\’ }
}
})
console.log(stringify)
const objString = stringify({
id: 1, name: \’shenfq\’
})
console.log(objString) // {“id”:1,”name”:”shenfq”}
经过 build 构造后,返回的序列化方法如下:
function $String (i) {
return \'”\’ i \'”\’
}
function $Number (i) {
var num = Number(i)
if (isNaN(num)) {
return \’null\’
} else {
return String(num)
}
}
function $Null (i) {
return \’null\’
}
// 序列化方法
function $main (obj) {
var json = \'{\’
json = \'”id”:\’
json = $Number(obj.id)
json = \’,\’
json = \'”name”:\’
json = $String(obj.name)
json = \’}\’
return json
}
可以看到,有 schema 做支撑,序列化的逻辑瞬间变得无比简单,最后得到的 JSON 字符串只保留需要的属性,简洁高效。我们回过头再看看 buildObject 是如何生成 $main 内的代码的:
function buildObject (schema, code, name) {
// 构造一个函数
code = `
function ${name} (obj) {
var json = \'{\’`
var laterCode = \’\’
// 遍历 schema 的属性
const { properties } = schema
Object.keys(properties).forEach((key, i, a) => {
// key 需要加上双引号
code = `
json = \’${$String(key)}:\’`
// 通过 nested 转化 value
const value = properties[key]
const result = nested(laterCode, name, `.${key}`, value)
code = result.code
laterCode = result.laterCode
if (i < a.length – 1) {
code = \’json = \’,\’\’
}
})
code = `
json = \’}\’
return json
}`
code = laterCode
return code
}
function nested (laterCode, name, key, schema) {
var code = \’\’
var funcName
// 判断 value 的类型,不同类型进行不同的处理
const type = schema.type
switch (type) {
case \’null\’:
code = `
json = $Null()`
break
case \’string\’:
code = `
json = $String(obj${key})`
break
case \’number\’:
case \’integer\’:
code = `
json = $Number(obj${key})`
break
case \’object\’:
// 如果 value 为一个对象,需要一个新的方法进行构造
funcName = (name key).replace(/[-.[]]/g, \’\’)
laterCode = buildObject(schema, laterCode, funcName)
code = `
json = ${funcName}(obj${key})`
break
case \’array\’:
funcName = (name key).replace(/[-.[]]/g, \’\’)
laterCode = buildArray(schema, laterCode, funcName)
code = `
json = ${funcName}(obj${key})`
break
default:
throw new Error(`${type} unsupported`)
}
return {
code,laterCode
}
}
其实就是对 type 为 “object” 的 properties 进行一次遍历,然后针对 value 不同的类型进行二次处理,如果碰到新的对象,会构造一个新的函数进行处理。
// 如果包含子对象
const stringify = build({
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
id: { type: \’number\’ },
info: {
type: \’object\’,
properties: {
age: { type: \’number\’ },
name: { type: \’string\’ },
}
}
}
})
console.log(stringify.toString())
function $main (obj) {
var json = \'{\’
json = \'”id”:\’
json = $Number(obj.id)
json = \’,\’
json = \'”info”:\’
json = $maininfo(obj.info)
json = \’}\’
return json
}
// 子对象会通过另一个函数处理
function $maininfo (obj) {
var json = \'{\’
json = \'”age”:\’
json = $Number(obj.age)
json = \’,\’
json = \'”name”:\’
json = $String(obj.name)
json = \’}\’
return json
}
总结
当然,fastify 之所以号称自己快,内部还有一些其他的优化方法,例如,在路由库的实现上使用了 Radix Tree 、对上下文对象可进行复用(使用 middie 库)。
联系信息:邮箱aoxolcom@163.com或见网站底部。












请登录后发表评论
注册
社交帐号登录