入口
Laravel启动后,会先加载服务提供者、中间件等组件,在查找路由之前因为我们使用的是门面,所以先要查到Route的实体类。
注册
第一步当然还是通过服务提供者,因为这是laravel启动的关键,在 RouteServiceProvider 内加载路由文件。
protected function mapApiRoutes() { Route::prefix('api') ->middleware('api') ->namespace($this->namespace) // 设置所处命名空间 ->group(base_path('routes/api.php')); //所得路由文件绝对路径 }
首先require是不可缺少的。因路由文件中没有命名空间。 IlluminateRoutingRouter 下方法
protected function loadRoutes($routes) { if ($routes instanceof Closure) { $routes($this); } else { $router = $this; require $routes; } }
随后通过路由找到指定方法,依旧是 IlluminateRoutingRouter 内有你所使用的所有路由相关方法,例如get、post、put、patch等等,他们都调用了统一的方法 addRoute
public function addRoute($methods, $uri, $action) { return $this->routes->add($this->createRoute($methods, $uri, $action)); }
之后通过 IlluminateRoutingRouteCollection addToCollections 方法添加到集合中
protected function addToCollections($route) { $domainAndUri = $route->getDomain().$route->uri(); foreach ($route->methods() as $method) { $this->routes[$method][$domainAndUri] = $route; } $this->allRoutes[$method.$domainAndUri] = $route; }
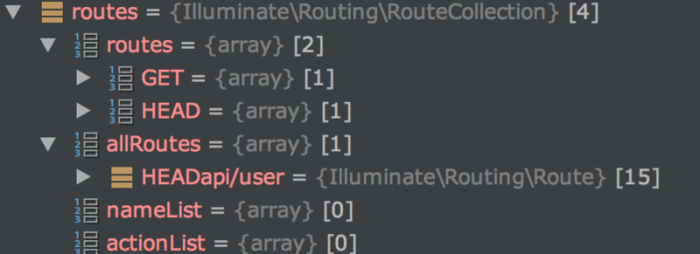
添加后的结果如下图所示
实例化
依旧通过反射加载路由指定的控制器,这个时候build的参数$concrete = AppApiControllersXxxController
public function build($concrete) { // If the concrete type is actually a Closure, we will just execute it and // hand back the results of the functions, which allows functions to be // used as resolvers for more fine-tuned resolution of these objects. if ($concrete instanceof Closure) { return $concrete($this, $this->getLastParameterOverride()); } $reflector = new ReflectionClass($concrete); // If the type is not instantiable, the developer is attempting to resolve // an abstract type such as an Interface of Abstract Class and there is // no binding registered for the abstractions so we need to bail out. if (! $reflector->isInstantiable()) { return $this->notInstantiable($concrete); } $this->buildStack[] = $concrete; $constructor = $reflector->getConstructor(); // If there are no constructors, that means there are no dependencies then // we can just resolve the instances of the objects right away, without // resolving any other types or dependencies out of these containers. if (is_null($constructor)) { array_pop($this->buildStack); return new $concrete; } $dependencies = $constructor->getParameters(); // Once we have all the constructor's parameters we can create each of the // dependency instances and then use the reflection instances to make a // new instance of this class, injecting the created dependencies in. $instances = $this->resolveDependencies( $dependencies ); array_pop($this->buildStack); return $reflector->newInstanceArgs($instances); }
这时将返回控制器的实例,下面将通过url访问指定方法,一般控制器都会继承父类 IlluminateRoutingController ,laravel为其设置了别名 BaseController
public function dispatch(Route $route, $controller, $method) { $parameters = $this->resolveClassMethodDependencies( $route->parametersWithoutNulls(), $controller, $method ); if (method_exists($controller, 'callAction')) { return $controller->callAction($method, $parameters); } return $controller->{$method}(...array_values($parameters)); }
Laravel通过controller继承的callAction去调用子类的指定方法,也就是我们希望调用的自定义方法。
public function callAction($method, $parameters) { return call_user_func_array([$this, $method], $parameters); }
© 版权声明
本文刊载的所有内容,包括文字、图片、音频、视频、软件、程序、以及网页版式设计等部门来源于互联网,版权均归原作者所有!本网站提供的内容服务于个人学习、研究或欣赏,以及其他非商业性或非盈利性用途,但同时应遵守著作权法及其他相关法律的规定,不得侵犯本网站及相关权利人的合法权利。
联系信息:邮箱aoxolcom@163.com或见网站底部。
联系信息:邮箱aoxolcom@163.com或见网站底部。
THE END












请登录后发表评论
注册
社交帐号登录