查看mysql 事务隔离级别
mysql> show variables like '%isolation%'; +---------------+----------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+----------------+ | tx_isolation | READ-COMMITTED | +---------------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到当前的事务隔离级别为 READ-COMMITTED 读提交
下面看看当前隔离级别下的事务隔离详情,开启两个查询终端A、B。
下面有一个order表,初始数据如下
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
第一步,在A,B中都开启事务
mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
第二步查询两个终端中的number值
A
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
B
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
第三步将B中的number修改为2,但不提交事务
mysql> update `order` set number=2; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
第四步查询A中的值
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 1 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
发现A中的值并没有修改。
第五步,提交事务B,再次查询A中的值
B
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
A
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
发现A中的值已经更改
第六步,提交A中的事务,再次查询A,B的值。
A
mysql> commit; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
B
mysql> select * from `order`; +----+--------+ | id | number | +----+--------+ | 13 | 2 | +----+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
发现A,B中的值都更改为2了。
下面给一个简单的示意图
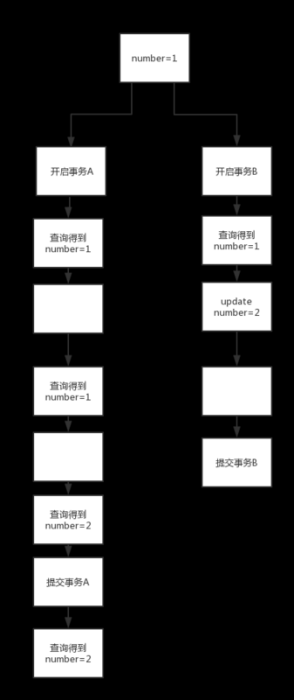
我们可以看到,在事务隔离级别为读已提交 的情况下,当B中事务提交了之后,即使A未提交也可以读到B事务提交的结果。这样解决了脏读的问题。
© 版权声明
本文刊载的所有内容,包括文字、图片、音频、视频、软件、程序、以及网页版式设计等部门来源于互联网,版权均归原作者所有!本网站提供的内容服务于个人学习、研究或欣赏,以及其他非商业性或非盈利性用途,但同时应遵守著作权法及其他相关法律的规定,不得侵犯本网站及相关权利人的合法权利。
联系信息:邮箱aoxolcom@163.com或见网站底部。
联系信息:邮箱aoxolcom@163.com或见网站底部。
THE END













请登录后发表评论
注册
社交帐号登录